Your basket is currently empty!



APPETITE CONTROL
FEEL FULL FIBRE APPETITE CONTROL
£21.99
- All in One Digestion & Weight Control
- Appetite Suppressant for Portion Control
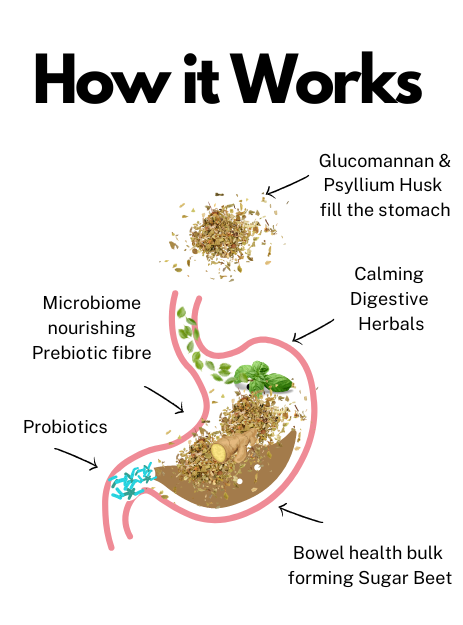
- Soluble Fibres Glucomannan & Psyllium Husk
- Prebiotic Fibre Inulin to feed your gut microbiome
- Sugar Beet Fibre for Bowel Function
- Amino Acid L-Glutamine building blocks of intestine health & immunity
- Probiotics
- Traditional Digestive Herbs Ginger, Peppermint & Fennel Seed




FEEL PRETTY FROM WITHIN
Looking & Feeling Good Really Does Start on the Inside!

Feel Full Fibre
Take 30-60 Minutes Before Meals for Natural Feel Full Appetite Control

Be Pretty Regular
Be Pretty Regular with Bowel supporting Sugar Beet Fibre

Gut Microbiome
Gut Healthy Prebiotic Fibre and Probiotic Cultures

Digestive Detox
Traditional Herbals to support Smooth Running Digestive Detox Pathways
Appetite Benefits
Appetite Benefits
+
DAILY NUTRITION
Increase your daily fibre intake. Most people are only consuming around half of the recommended daily 30g of fibre.
Pretty Full Fibre Appetite control combines the nutritional goodness and benefits of 4 fibre types to give your body what it needs to look and feel pretty good from the inside out.
WEIGHT LOSS APPETITE CONTROL
Appetite Control Feel Full Fibre supports weight loss and appetite control in several ways which include promoting the release of satiety hormones, feelings of fullness and delayed stomach emptying.
Glucomannan promotes control of energy intake and studies show it can reduces the risk of developing obesity and can result in significant weight loss in overweight and obese individuals.
Appetite’s blend of nutrients also feed friendly gut bacteria. Healthy gut bacteria have been linked to a reduced risk of obesity.
All this helps support calorie and appetite control without you even having to think about it.
DIGESTIVE SUPPORT
In addition to containing soluble and insoluble digestion-loving fibres, Appetite also contains probiotic cultures and prebiotic fibre – (prebiotics the food that nourishes your gut microbiome)
Studies show that prebiotic and probiotics can improve IBS symptoms.
Appetite Control has added calming, muscle relaxing and nourishing digestive herbals Peppermint, Ginger and Fennel Seed that have been used traditionally for centuries for digestive ailments.
BOWEL HEALTH & CONSTIPATION
Supports bowel health and increases faecal bulk which may also be helpful for constipation.
FREE FROM SUPPLEMENT
Under 10 calories per serving. Natural and free from artificial nasties. Vegan and gluten free.
How many servings
+
Pretty Pea Appetite control powdered formula comes in 180g pot and contains 36 servings.
How to use
+
Add 1 serving (a heaped teaspoon) to a small amount of water or juice (1/4 glass).
Mix slowly in all directions until its turns into a smooth paste. Continue to stir as more liquid is added until the glass is full or your desired consistency is achieved.
Consume immediately and follow with another large glass of water to ensure the contents reach the stomach quickly where it will naturally begin to expand promoting a natural feeling of fullness.
To be taken approximately 30-60 minutes before each meal (3x daily) for best weight loss results.
For those with a sensitive digestion or perhaps not used to much fibre on a regular basis then it can be advisable to start on a reduced dose, (half dose) for 7 days and then increasing every 3-4 days as the body acclimatises to the fibre content.
What’s Inside?
Glucomannan
+
EFSA Approved Weight Loss Supplement
High in dietary fibre, Glucomannan is particularly effective for weight loss and weight management. Studies show that at the correct dose it can result in significant weight loss in overweight and obese individuals.
With many supplements nowadays purporting to support weight loss, Glucomannan is approved by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) to support weight loss, using 3g per day, at 1g x 3 to be taken before each meal and in the context of a calorie controlled diet.
It’s a natural water soluble fibre extracted from the Konjac plant with an exceptional ability to absorb water up to 50 times its weight.
Glucomannan differs from most other soluble fibres, it is exceptionally viscous, making it particularly effective for weight loss. It works by absorbing water in your stomach and then gently expands.
For weight loss benefits glucomannan needs to be taken before meals.
Timings will vary per individual and recommended ranges are from 15 minutes to 1 hour before meals.
Glucomannan and Heart Disease
Glucomannan may improve some heart disease risk factors. It contributes to the maintenance of normal blood cholesterol levels with a daily intake of 4g glucomannan
According to a systematic review of 14 studies, glucomannan can lower:
- Total cholesterol by 19 mg/dL (0.5 mmol/L).
- “Bad” LDL cholesterol by 16 mg/dL (0.4 mmol/L).
- Triglycerides by 11 mg/dL (0.12 mmol/L).
- Fasting blood sugar by 7.4 mg/dL (0.4 mmol/L)
Glucomannan and Constipation
Glucomannan has also been successfully used for constipation.
GLUCOMANNAN SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS
Glucomannan is considered safe and well tolerated.
It must be taken with 1-2 glasses of water to ensure it reaches the stomach before expanding.
This is especially important for people with swallowing difficulties when ingesting as it may cause choking or blockage of the throat.
For those who do not consume much fibre on a daily basis or may have a sensitive digestion may want to start on a half dose and build up slowly to enable the body to acclimatize.
These people may occasionally experience mild side effects, such as flatulence, bloating, soft stools or diarrhoea, but these effects are uncommon and transient in nature as the body adapts to the fibre content.
Weight Loss 6 Ways
+
How Glucomannan supports Weight Loss:
1. Leaves you feeling naturally full (satiety) and satisfied as it takes up space in the stomach, helping reduce food intake
2. It delays stomach emptying, keeping you feeling fuller for longer, decreasing hunger and the urge to snack
3. It’s very low in calories
4. Glucomannan reduces the absorption of protein and fat
5. Glucomannan feeds the friendly bacteria in your intestine, which turn it into short-chain fatty acids like butyrate, which have shown to protect against fat gain in some animal studies
6. Feeding your gut bacteria may also have other benefits. Studies have shown a correlation between body weight and altered gut bacteria
Reduction in body weight is obtained with a daily intake of 3 g of glucomannan in three doses of 1 g each, together with 1-2 glasses of water, before meals and in the context of an energy-restricted diet.
Psyllium Husk
+
Psyllium Husk
Psyllium husk is a herb that has long been used in traditional medicine in India and China.
Its seed husk is used as a laxative and stool softener and to help reduce cholesterol.
Psyllium seed husks absorb water in the stomach and form a large mass. This mass stimulates the bowel in people with constipation. In people with diarrhoea, it can slow down the bowel and reduce bowel movements. This mass can also reduce the amount of cholesterol that is absorbed into the body.
Psyllium is commonly used as a stool softener in people with constipation and hemorrhoids.
How effective is Psyllium?
Natural Medicines Comprehensive Database rates effectiveness based on scientific evidence according to the following scale: Effective, Likely Effective, Possibly Effective, Possibly Ineffective, Likely Ineffective, Ineffective, and Insufficient Evidence to Rate.
The effectiveness ratings for BLOND PSYLLIUM are as follows:
Effective for…
Constipation. Taking blond psyllium by mouth, alone or as a combination product, can relieve constipation and improve stool consistency.
Likely Effective for…
Heart disease. Blond psyllium is a soluble fibre. Eating foods high in soluble fibre as part of a low-fat, low-cholesterol diet can help prevent heart disease. You must eat at least 7 grams of psyllium husk daily to reduce the risk for heart disease.
High levels of cholesterol or other fats (lipids) in the blood (hyperlipidemia). Taking blond psyllium by mouth reduces low density lipoprotein (LDL or “bad”) cholesterol in people with mild to moderate high cholesterol. But it seems to be less effective in older people.
Possibly effective for…
Diabetes. Taking blond psyllium by mouth can improve blood sugar control in people with diabetes. But it’s not clear if it helps prevent diabetes.
Diarrhoea. Taking blond psyllium by mouth seems to reduce diarrhoea symptoms.
Hemorrehoids. Taking blond psyllium by mouth seems to relieve bleeding and pain in people with hemorrehoids.
A long-term disorder of the large intestines that causes stomach pain (irritable bowel syndrome or IBS). Taking blond psyllium by mouth can relieve constipation and improve stomach pain, diarrhoea, and overall well-being in people with IBS. It might take up to four weeks for it to help.
There’s More….
Weight Loss Guidance
+
Weight loss takes time. Average rate of weight loss (without supplements) for someone following a calorie controlled diet is 1lb per week.
Weight loss does get harder with age as the body changes. It’s no longer just a case of calories in v calories out . Whilst eating a bit less and moving more is the obvious starting point – being in a calorie deficit is just one variable. Weight loss is complex with many variables involved.
Examples of other common variables impacting womens weight loss include: underlying health issues, medications, hormone imbalances, insulin resistance, stress, sleep issues, reduced muscle mass and slower metabolism. Any of these can make weight loss feel almost impossible at times. You can read more at our BLOG page Reason’s You’re Not Losing Weight
Weight loss is not linear – it doesn’t follow a straight path. Results can fluctuate each week, even daily. The scales can even fluctuate up to 5lb on any given day. Focus on the bigger overall picture.
The scales are not your only measure of success, how you feel, how your clothes fit, your energy levels, improved sleep etc all affect how we feel and are real results that matter.
If you do want to use scales we recommend using bio-impedance scales, as these are helpful in measure other factors that include BMR (basal metabolic rate), muscle mass and water levels. These scales can help shift your focus to increasing hydration and all important muscle mass (which in turn affects your metabolism) and also understanding your BMR – the minimum amount of calories your body needs.
You can achieve ANYTHING with persistence and consistency.
Sugar Beet Fibre
+
When your digestive system is moving regularly you just feel better, less bloated and sluggish as the accumulation of toxins that put a stress load on the body are excreted via our bodily waste.
The digestive system is also home to around 70-80% of our immune system and happy hormone serotonin.
Who needs Sugar Beet Fibre
This type of fibre contributes to normal bowel function and an increase in faecal bulk which can make for easier bowel movements.
Sugar Beet can increase in faecal bulk in two ways:
1. The insoluble components of the fibre increase bulk by absorbing water in the large intestine, plus
2. The soluble components are fermented by bacteria in the large intestine leading to an increase in bacterial mass
Peppermint Leaf
+
Peppermint is a traditionally used herb with medicinal, phytochemical and multiple biological activities including antibacterial, antiviral, and anti-inflammatory properties.
Used for centuries as a treatment for gastrointestinal ailments, studies indicate that peppermint relaxes the digestive system, gut spasms and may ease pain. and may relieve digestive symptoms, such as bloating, gas, and indigestion and act as a carminative (i.e. reliever of flatulence).
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a chronic functional bowel disorder affecting 5.7% of the general population. Most patients relate their symptoms of IBS to foods they consume, however, although some foods may trigger symptoms, others foods, such as peppermint may provide symptom relief.
A 2014 review of nine studies of people with IBS treated with peppermint oil for at least 2 weeks concluded that peppermint provided significantly better symptom relief than a placebo.
Menstrual Cramps
Acting as a muscle relaxant, peppermint may relieve menstrual cramps.
In one study of females with painful periods, peppermint extract capsules were found to be as effective as a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug in reducing the intensity and duration of pain.
Fennel Seed
+
Fennel seeds act as a gentle warming agent for delicate stomachs.
Fennel is also a carminative, aromatic, anti-spasmodic, antibacterial, antifungal, digestive and gut soother, which has mild stimulant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Fennel is packed full of fibre and important nutrients such as vitamin C, calcium, magnesium, potassium and manganese.
Appetite Control
Fennel is a herb also used to help curb appetite.
A study of healthy women found that those who drank 250 ml of tea made with 2 grams of fennel seeds before eating were significantly less hungry and consumed fewer calories during the meal than those who drank a placebo tea.
Menopause symptoms
Fennel has strong estrogenic properties, meaning that it acts similar to the hormone estrogen.
A review of 10 studies found that fennel may improve sexual function and satisfaction in menopausal women, as well as relieve hot flushes, sleep disturbances along with other menopause symptoms.
Ginger Root
+
Ginger is a member of a plant family that includes cardamom and turmeric with powerful medicinal properties.
Indians and Chinese are believed to have produced ginger as a tonic root for over 5000 years to treat many ailments such as colds, nausea, arthritis, migraines and hypertension.
The medicinal, chemical, and pharmacological properties of ginger have been extensively reviewed.
Benefits of Ginger
It’s main bioactive compound, Gingerol, has powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects and responsible for many of it’s medicinal properties.
Ginger has a long history of use traditional and alternative medicine and is typically known for:
Calming remedy for indigestion, nausea & upset stomach
Help fight the flu and common cold
Fight inflammation and gastrointestinal ailments
Pain-relieving effects
Relieve headaches and migraines
Ginger and Weight Loss
Ginger may also play a role in weight loss. According to studies, Ginger has positive effects on weight control, obesity prevention, and energy metabolism.
A 2019 review found that ginger supplementation significantly reduced body weight, the waist-hip ratio, and the hip ratio in people with overweight or obesity.
It’s anti-inflammatory properties can also counter inflammation. Research indicates that obesity can bring on oxidative stress and inflammation.
A meta-analysis of studies demonstrated that ginger intake reduced body weight, waist to hip ratio, fasting glucose and increased HDL-cholesterol.
Ginger also has appetite-suppressing properties.
Ginger & Digestion
Ginger has also been used traditionally as a digestive herb with a long history in treating digestive upset and pain.
It supports digestion being a highly effective carminative, a substance that promotes the elimination of excessive gas from the digestive system and soothes the intestinal tract.
Prebiotic Inulin Fibre
+
Inulin (Fructo-Oligosaccharides), is known as a prebiotic fibre.
Prebiotic fibres are non-digestible carbohydrates that promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut.
Studies show that prebiotics offer the potential to modify the gut microbial balance in such a way as to bring direct health benefits cheaply and safely.
Benefits of Prebiotics
Prebiotics are like food for your gut microbiome as they are utilized by the intestinal microbiota to confer health benefits.
Consuming prebiotics may benefit obesity and associated co-morbidities by improving or normalizing the dysbiosis of the gut microbiota.
Studies have shown that prebiotic fibres increased Firmicutes and decreased Bacteroidetes, a profile often associated with a leaner body type.
Probiotics
+
Probiotics have been defined by the World Health Organization as “live microoganisms which when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit on the host.”
Sleep, Mood & Anxiety
A 2020 review of studies found a correlation between probiotic bacteria and mood and sleep quality improvement in those who experienced anxiety and depression.
Hot Flushes & Night Sweats
A 2017 study of women found that taking probiotics alongside red clover supplements may help reduce vasomotor symptoms, like hot flushes and night sweats.
Osteoarthritis
A 2021 review of studies found that probiotics may help increase bone mineral density of the lumbar spine in postmenopausal women.
Gut Dysbiosis & Weight Gain
An imbalance of healthy and unhealthy microbes is known as gut dysbiosis, and it may contribute to weight gain.
Certain Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli, found in probiotics, can help prevent leaky gut syndrome sealing the gaps between intestinal cells.
Gut Dysbiosis & Immunity
A large number of diseases have recently been associated with intestinal dysbiosis (imbalanced gut microbiome).
By communicating with immune cells, the gut microbiome can control how your body responds to infection by communicating with immune cells.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Studies show that Probiotics that contain Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli may also help reduce IBS symptoms.
L-Glutamine
+
What is L-Glutamine
L-glutamine, (glutamine), is the most abundant amino acid in the body. This protein building block is important for the immune system and intestinal health (the intestines are considered the largest portion of the immune system).
Studies show that Glutamine is essential for immune health, intestinal health cell function and metabolism.
Who needs L-Glutamine
When the body is under stress it’s requirements for glutamine appear to exceed the individual’s ability to produce sufficient amounts of this amino acid.
It’s therefore, considered a conditionally essential amino acid, meaning that it must be obtained from the diet (or supplement) when the body is under stress, including injury or illness.
Studies have also reported that glutamine supplements may improve health, decrease infections and lead to shorter hospital stays after surgery.
L-Glutamine, Immunity and Leaky Gut
Glutamine is an important energy source for intestinal and immune cells, including white blood cells.
It helps maintain the barrier between the inside of your intestines and the rest of your body, thereby protecting against what’s known as a leaky gut.
This barrier prevents harmful bacteria or toxins from moving from your intestines into the rest of your body.
L-Glutamine and Weight Loss
Studies link glutamine supplements to increased weight loss.
A 6 week study of people with type 2 diabetes found that taking 30 grams of glutamine powder daily improved multiple risk factors for heart disease and reduced both body and belly fat.
Similarly, a 2-week study using the same amount of glutamine observed decreased waist circumference, a marker for belly fat, in 39 people with overweight or obesity.
In another 4 week study, women taking glutamine supplements experienced significant reductions in body weight and belly fat without making other dietary or lifestyle changes.
How L-Glutamine supports Weight Loss
L-glutamine supports weight loss through several mechanisms.
Studies indicate that L-glutamine supplements alter the composition of beneficial bacteria (gut microbiome) in the digestive tract
The gut microbiome plays a central role in many aspects of health, including weight management.
Glutamine may protect against inflammation, which is linked to many chronic conditions, including obesity.
Studies show that L-glutamine may improve blood sugar control.
Studies suggest that glutamine enhances insulin sensitivity, improving the body’s ability to use insulin efficiently. Impaired insulin sensitivity is associated with a higher risk of weight gain and obesity.
As it’s a protein building block, by having enough glutamine in your system you’re also better able to lose weight while maintaining muscle tissue.
Digestive Support
L-Glutamine is not only the most abundant amino acid for muscle tissue but it’s also pretty much one of the most important and abundant nutrients in your entire body as it heals all the tissue in your body, and especially those irritated tissues in the digestive tract and is known to relieve bloating.
Essential for healing the gut lining and leaky gut, malabsorption and inflammatory bowel issues such as IBS because of it’s ability to maintain the integrity of the intestinal wall.
L-glutamine can also boost immune cell activity in the gut, helping prevent infection and inflammation, as well as soothing the intestinal tissue.
Safety & Contraindications
Results may vary from person to person.
Store in a cool dry place, out of the reach of children.
Best before end: see base of container.
Caution: Do not exceed the recommended daily intake.
Not recommended to take alongside other products containing Glucomannan. (Meno Weight/Pretty From Within)
A food supplement should not be used as a substitute for a varied, balanced diet and healthy lifestyle. Always consult your GP before taking food supplements if you are taking medication or have an existing medical condition.
GLUCOMANNAN SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS
Glucomannan is considered safe and well tolerated.
Warning: Appetite must be taken with 1-2 glasses of water to ensure it reaches the stomach before expanding.
This is especially important for people with swallowing difficulties when ingesting as it may cause choking or blockage of the throat.
For those who do not consume a lot of fibre on a regular basis or have a sensitive digestion it’s advisable to start on a half dose and build up gradually to enable the body to acclimatize to the increased fibre intake.
These people may occasionally experience mild side effects, such as flatulence, bloating, soft stools or diarrhoea, but these effects are transient and uncommon.
As with all supplements, if you feel unwell whilst taking this supplement discontinue use immediately and seek medical advice.
References
Gut microbiota composition correlates with changes in body fat content due to weight loss – PubMed (nih.gov)
The Prebiotic Potential of Inulin-Type Fructans: A Systematic Review – PubMed (nih.gov)
Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of a health claim related to sugar beet fibre and increasing faecal bulk pursuant to Article 13(5) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006 (wiley.com)
Psyllium: a useful functional ingredient in food systems – PubMed (nih.gov)
Dietary fiber decreases the metabolizable energy content and nutrient digestibility of mixed diets fed to humans – PubMed (nih.gov)
Does ginger supplementation lower blood pressure? A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials – PubMed (nih.gov)
Peppermint oil for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis – PubMed (nih.gov)
Review article: probiotics and prebiotics in irritable bowel syndrome – PubMed (nih.gov)
Evaluation of mint efficacy regarding dysmenorrhea in comparison with mefenamic acid: A double blinded randomized crossover study – PubMed (nih.gov)
Dietary fibres in the regulation of appetite and food intake. Importance of viscosity. Appetite. 2011 Feb;56(1):65-70. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2010.11.147. Epub 2010 Nov 27. PMID: 21115081.Beck EJ, Tapsell LC, Batterham MJ, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21115081/
Increases in peptide Y-Y levels following oat beta-glucan ingestion are dose-dependent in overweight adults. Nutr Res. 2009 Oct;29(10):705-9. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2009.09.012. PMID: 19917449.
How to get more fibre into your diet – NHS (www.nhs.uk)
Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of a health claim related to sugar beet fibre and increasing faecal bulk pursuant to Article 13(5) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006 (wiley.com)
Effect of Fennel on the Health Status of Menopausal Women: A Systematic and Meta-analysis – PMC (nih.gov)
Gut microbiota, obesity and diabetes – PubMed (nih.gov)
A Descriptive Overview of the Medical Uses Given to Mentha Aromatic Herbs throughout History – PMC (nih.gov)
Peppermint oil in irritable bowel syndrome – PubMed (nih.gov)
Peppermint oil for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis – PubMed (nih.gov)
Evaluation of mint efficacy regarding dysmenorrhea in comparison with mefenamic acid: A double blinded randomized crossover study – PubMed (nih.gov)
The Wonderful Activities of the Genus Mentha: Not Only Antioxidant Properties – PMC (nih.gov)
Food supplements and diet as treatment options in irritable bowel syndrome – PubMed (nih.gov)
Glucomannan and obesity: a critical review – PubMed (nih.gov)
The role of carbohydrates in insulin resistance. J Nutr. 2001 Oct;131(10):2782S-2786S. doi: 10.1093/jn/131.10.2782S. PMID: 11584106.
Meta-analysis of probiotics for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome – PubMed (nih.gov)
Dietary fiber decreases the metabolizable energy content and nutrient digestibility of mixed diets fed to humans. J Nutr. 1997 Apr;127(4):579-86. doi: 10.1093/jn/127.4.579. PMID: 9109608.
Colonic health: fermentation and short chain fatty acids. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2006 Mar;40(3):235-43. doi: 10.1097/00004836-200603000-00015. PMID: 16633129.
Gut microbiota, obesity and diabetes – PubMed (nih.gov)
The Wonderful Activities of the Genus Mentha: Not Only Antioxidant Properties – PMC (nih.gov)
Ginger on Human Health: A Comprehensive Systematic Review of 109 Randomized Controlled Trials – PMC (nih.gov)
Effect of Ginger on Inflammatory Diseases – PMC (nih.gov)
The effects of ginger intake on weight loss and metabolic profiles among overweight and obese subjects: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials – PubMed (nih.gov)
Dietary fiber and weight regulation. Nutr Rev. 2001 May;59(5):129-39. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.2001.tb07001.x. PMID: 11396693.
Butyrate improves insulin sensitivity and increases energy expenditure in mice. Diabetes. 2009 Jul;58(7):1509-17. doi: 10.2337/db08-1637. Epub 2009 Apr 14. PMID: 19366864; PMCID: PMC2699871.
Experiences with three different fiber supplements in weight reduction. Med Sci Monit. 2005 Jan;11(1):PI5-8. PMID: 15614200.
Probiotic supplements and bone health in postmenopausal women: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials | BMJ Open
Fennel (Foeniculum vulgare) and Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) Tea Drinking Suppresses Subjective Short-term Appetite in Overweight Women – PMC (nih.gov)
Glutamine: Metabolism and Immune Function, Supplementation and Clinical Translation – PMC (nih.gov)
Foeniculum vulgare: A comprehensive review of its traditional use, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and safety – ScienceDirect
Ginger on Human Health: A Comprehensive Systematic Review of 109 Randomized Controlled Trials – PMC (nih.gov)
The Amazing and Mighty Ginger – Herbal Medicine – NCBI Bookshelf (nih.gov)
Dysbiosis and the immune system – PubMed (nih.gov)
Gut microbiota, obesity and diabetes – PubMed (nih.gov)
Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of a health claim related to sugar beet fibre and increasing faecal bulk pursuant to Article 13(5) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006 (wiley.com)
Effect of glucomannan on plasma lipid and glucose concentrations, body weight, and blood pressure: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008 Oct;88(4):1167-75. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/88.4.1167. PMID: 18842808.
Effect of glucomannan on obese patients: a clinical study. Int J Obes. 1984;8(4):289-93. PMID: 6096282
Effects of glutamine supplementation on patients undergoing abdominal surgery – PubMed (nih.gov)
EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA); Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of a health claim related to sugar beet fibre and increasing faecal bulk pursuant to Article 13(5) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006. EFSA Journal 2011; 9(12):2468. [8 pp.]. doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2011.2468.
The Prebiotic Potential of Inulin-Type Fructans: A Systematic Review. Adv Nutr. 2022 Mar;13(2):492-529. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmab119. Epub 2023 Feb 10. PMID: 34555168; PMCID: PMC8970830.
Gut microbiota, obesity and diabetes – PubMed (nih.gov)
Prebiotic fiber modulation of the gut microbiota improves risk factors for obesity and the metabolic syndrome – PubMed (nih.gov)
Food & mood: a review of supplementary prebiotic and probiotic interventions in the treatment of anxiety and depression in adults – PMC (nih.gov)
Review article: prebiotics in the gastrointestinal tract. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006 Sep 1;24(5):701-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2006.03042.x. PMID: 16918875.
Psyllium: a useful functional ingredient in food systems. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022;62(2):527-538. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1822276. Epub 2020 Sep 21. PMID: 32951436.
The role of carbohydrates in insulin resistance. J Nutr. 2001 Oct;131(10):2782S-2786S. doi: 10.1093/jn/131.10.2782S. PMID: 11584106.
Nutrition, anabolism, and the wound healing process: an overview. Eplasty. 2009;9:e9. Epub 2009 Feb 3. PMID: 19274069; PMCID: PMC2642618.
Glutamine: Metabolism and Immune Function, Supplementation and Clinical Translation. Nutrients. 2018 Oct 23;10(11):1564. doi: 10.3390/nu10111564. PMID: 30360490; PMCID: PMC6266414.
Amino acids: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia
Effects of glutamine supplementation on patients undergoing abdominal surgery. Chin Med Sci J. 2009 Mar;24(1):55-9. doi: 10.1016/s1001-9294(09)60060-2. PMID: 19382426.
Glutamine as an immunonutrient. Yonsei Med J. 2011 Nov;52(6):892-7. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2011.52.6.892. PMID: 22028151; PMCID: PMC3220259.
Glutamine and intestinal barrier function. Amino Acids. 2015 Oct;47(10):2143-54. doi: 10.1007/s00726-014-1773-4. Epub 2014 Jun 26. PMID: 24965526.
Glutamine: an essential amino acid for the gut. Nutrition. 1996 Nov-Dec;12(11-12 Suppl):S78-81. doi: 10.1016/s0899-9007(97)85206-9. PMID: 8974125.
Effect of glutamine supplementation on cardiovascular risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes. Nutrition. 2015 Jan;31(1):119-26. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2014.05.014. Epub 2014 Jun 23. PMID: 25466655.
Oral Glutamine Supplementation Reduces Obesity, Pro-Inflammatory Markers, and Improves Insulin Sensitivity in DIO Wistar Rats and Reduces Waist Circumference in Overweight and Obese Humans. Nutrients. 2019 Mar 1;11(3):536. doi: 10.3390/nu11030536. PMID: 30832230; PMCID: PMC6471297.
Glutamine supplementation favors weight loss in nondieting obese female patients. A pilot study. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2014 Nov;68(11):1264-6. doi: 10.1038/ejcn.2014.184. Epub 2014 Sep 17. PMID: 25226827.
The Role of Glutamine in the Complex Interaction between Gut Microbiota and Health: A Narrative Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 22;20(20):5232. doi: 10.3390/ijms20205232. PMID: 31652531; PMCID: PMC6834172.
The Gut Microbiome and Its Role in Obesity. Nutr Today. 2016 Jul-Aug;51(4):167-174. doi: 10.1097/NT.0000000000000167. PMID: 27795585; PMCID: PMC5082693.
Insights into the role of gut microbiota in obesity: pathogenesis, mechanisms, and therapeutic perspectives. Protein Cell. 2018 May;9(5):397-403. doi: 10.1007/s13238-018-0546-3. PMID: 29725936; PMCID: PMC5960470.
Obesity and inflammation: the linking mechanism and the complications. Arch Med Sci. 2017 Jun;13(4):851-863. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2016.58928. Epub 2016 Mar 31. PMID: 28721154; PMCID: PMC5507106.
A comprehensive insight into the effect of glutamine supplementation on metabolic variables in diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2020 Sep 25;17:80. doi: 10.1186/s12986-020-00503-6. PMID: 32983244; PMCID: PMC7517657.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/285772772_Metabolic_effects_of_glutamine_on_insulin_sensitivity
Insulin resistance in obesity: an overview of fundamental alterations. Eat Weight Disord. 2018 Apr;23(2):149-157. doi: 10.1007/s40519-018-0481-6. Epub 2018 Feb 3. PMID: 29397563.
Insulin Resistance. [Updated 2023 Aug 17]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507839/
Gut microbiota composition correlates with changes in body fat content due to weight loss – PubMed (nih.gov)
A review of supplementary prebiotic and probiotic interventions in the treatment of anxiety and depression in adults. BMJ Nutr Prev Health. 2020 Jul 6;3(2):351-362. doi: 10.1136/bmjnph-2019-000053. PMID: 33521545; PMCID: PMC7841823.
Combined Red Clover isoflavones and probiotics potently reduce menopausal vasomotor symptoms | PLOS ONE
Probiotic supplements and bone health in postmenopausal women: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials
Weerts ZZRM, Masclee AAM, Witteman BJM, Clemens CHM, Winkens B, Brouwers JRBJ, Frijlink HW, Muris JWM, De Wit NJ, Essers BAB, Tack J, Snijkers JTW, Bours AMH, de Ruiter-van der Ploeg AS, Jonkers DMAE, Keszthelyi D. Efficacy and Safety of Peppermint Oil in a Randomized, Double-Blind Trial of Patients With Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Gastroenterology. 2020 Jan;158(1):123-136. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.08.026. Epub 2019 Aug 27. PMID: 31470006.
Food supplements and diet as treatment options in irritable bowel syndrome – PubMed (nih.gov)
A Novel Delivery System of Peppermint Oil Is an Effective Therapy for Irritable Bowel Syndrome Symptoms. Dig Dis Sci. 2016 Feb;61(2):560-71. doi: 10.1007/s10620-015-3858-7. Epub 2015 Aug 29. PMID: 26319955; PMCID: PMC4729798. Food supplements and diet as treatment options in irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2020 Aug;32(8):e13951. doi: 10.1111/nmo.13951. PMID: 32697018.
Peppermint oil for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2014 Jul;48(6):505-12. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e3182a88357. PMID: 24100754.
Fennel (Foeniculum vulgare) and Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) Tea Drinking Suppresses Subjective Short-term Appetite in Overweight Women – PubMed (nih.gov)
Effect of Fennel on the Health Status of Menopausal Women: A Systematic and Meta-analysis – PubMed (nih.gov)
Anh NH, Kim SJ, Long NP, Min JE, Yoon YC, Lee EG, Kim M, Kim TJ, Yang YY, Son EY, Yoon SJ, Diem NC, Kim HM, Kwon SW. Ginger on Human Health: A Comprehensive Systematic Review of 109 Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients. 2020 Jan 6;12(1):157. doi: 10.3390/nu12010157. PMID: 31935866; PMCID: PMC7019938.
Ballester P, Cerdá B, Arcusa R, Marhuenda J, Yamedjeu K, Zafrilla P. Effect of Ginger on Inflammatory Diseases. Molecules. 2022 Oct 25;27(21):7223. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217223. PMID: 36364048; PMCID: PMC9654013.
The Amazing and Mighty Ginger. In: Benzie IFF, Wachtel-Galor S, editors. Herbal Medicine: Biomolecular and Clinical Aspects. 2nd edition. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2011. Chapter 7. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK92775/
Effect of ginger (Zingiber officinale) supplementation on oxidative stress parameters: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Food Biochem. 2021 Feb;45(2):e13612. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.13612. Epub 2021 Jan 17. PMID: 33458848.
The effects of ginger supplementation on markers of inflammatory and oxidative stress: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Phytother Res. 2020 Aug;34(8):1723-1733. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6638. Epub 2020 Mar 8. PMID: 32147845.
Does ginger supplementation lower blood pressure? A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Phytother Res. 2019 Jun;33(6):1639-1647. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6362. Epub 2019 Apr 11. PMID: 30972845.
The effects of ginger intake on weight loss and metabolic profiles among overweight and obese subjects: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(11):1753-1766. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1427044. Epub 2018 Feb 2. PMID: 29393665.
The effects of ginger intake on weight loss and metabolic profiles among overweight and obese subjects: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(11):1753-1766. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1427044. Epub 2018 Feb 2. PMID: 29393665.
Efficacy and Safety of Peppermint Oil in a Randomized, Double-Blind Trial of Patients With Irritable Bowel Syndrome – PubMed (nih.gov)