Your basket is currently empty!



Mind+ Brain Supplement
NOOTROPIC SUPPLEMENT
£25.99
Nootropic supplement combining 25 Brain food nutrients including Vitamin B12, B3, B5 with Ashwagandha KSM66, DHA, NAC, Ginkgo, Panax Ginseng, L-Theanine & many more power-packed nutrients to support normal:
Mental Performance
Cognitive & Neurological Function
Reduce Tiredness & Fatigue
Production of Thyroid Hormones

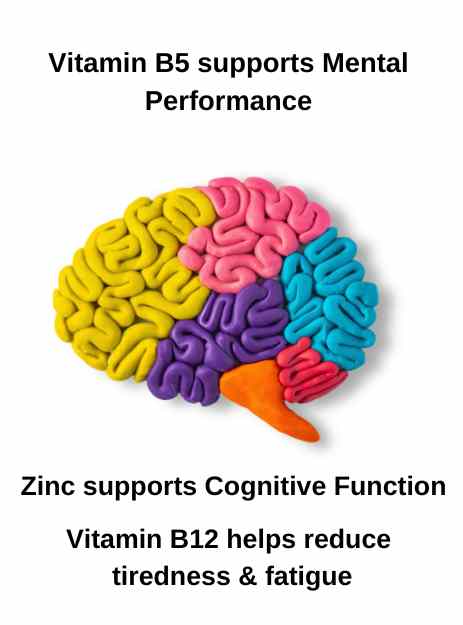


FEELING PRETTY POWERED STARTS FROM WITHIN
Elevating Your Brain Power with Neuro Nutrition!

Mental Performance
Contributes to normal Mental Performance

Cognitive Function
Contributes to normal Cognitive & Neurological Function

Energy Levels
Contributes to the Reduction of Tiredness & Fatigue

Psychological Function
Contributes to normal Psychological Function
Mind+ Nootropic Benefits
Brain Food Benefits
+
A natural nootropic and nutritional cognitive enhancer! MIND+ is a super-concentrated, powerful food supplement for the brain.
It contains a special combination of vitamin and mineral ingredients that support focus, concentration, mental performance, memory recall and energy levels.
It can support your ability to think more clearly and provides valuable additional nutritional energy to your brain and body – with a number of scientifically backed and EFSA approved health claims.
To boost its efficacy and provide additional nutrients synergistic herbal and nutritive allies have also been added to the formula.
These include: Korean Panax Ginseng, Guarana, Bacopa monnieri, Ginkgo leaf, Ashwagandha, Green tea leaf, Caffeine, L-Theanine, L-Tyrosine, N-Acetyl L-Carnitine, Rosemary leaf, DHA, Choline, Phosphatidylcholine, Cinnamon, Turmeric root (curcuminoids), Phosphatidyl serine and Black pepper.
How many servings
+
Contains 60 Vegetarian Easy Take Capsules
How to use
+
Take 2 capsules with a glass of water.
For best results take 45 minutes before food or 90 minutes after food.
Take no more than 6 capsules per day.
Do not exceed the recommended daily amount.
What’s Inside?
B Vitamins
+
Vitamin B3 (niacin) helps turn the food you eat into energy. Niacin is important for the development and function of the cells in your body.
Niacin contributes to normal psychological function, energy-yielding metabolism, functioning of the nervous system, the maintenance of mucous membranes, the maintenance of skin and the reduction of tiredness and fatigue.
Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid) helps turn the food you eat into the energy you need. It’s important for many functions in the body, especially making and breaking down fats.
Vitamin B5 contributes to normal energy-yielding metabolism, mental performance, synthesis and metabolism of steroid hormones, vitamin D and some neurotransmitters, and the reduction of tiredness and fatigue.
Vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin)
Vitamin B12 is a nutrient that helps keep your body’s blood and nerve cells healthy and helps make DNA, the genetic material in all of your cells. Vitamin B12 also helps prevent megaloblastic anemia, a blood condition that makes people tired and weak.
Vitamin B12 contributes to normal energy-yielding metabolism, functioning of the nervous system, homocysteine metabolism, psychological function, red blood cell formation, function of the immune system, the reduction of tiredness and fatigue and it has a role in the process of cell division
Folic acid contributes to normal psychological function, function of the immune system, the reduction of tiredness and fatigue, homocysteine metabolism, amino acid synthesis, blood formation, the process of cell division and maternal tissue growth during pregnancy.
Neuro Nutrients & Amino Acids
+
Choline is a nutrient found in many foods. Your brain and nervous system need it to regulate memory, mood, muscle control, and other functions. You also need choline to form the membranes that surround your body’s cells. You can make a small amount of choline in your liver, but most of the choline in your body comes from the food you eat.
Choline contributes to normal lipid metabolism (the breakdown and storage of fats for energy). Getting enough choline is necessary for proper liver function and to prevent Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Some studies have found a link between higher intakes of choline (and higher blood levels of choline) and better cognitive function (such as verbal and visual memory).
Iodine is a mineral found in some foods. Iodine contributes to normal cognitive function, energy-yielding metabolism, the production of thyroid hormones and thyroid function
The body needs iodine to make thyroid hormones. Thyroid hormones control the body’s metabolism and many other important functions. The body also needs thyroid hormones for proper bone and brain development during pregnancy and infancy.
Zinc is found in cells throughout the body and contributes to normal DNA synthesis, acid-base metabolism, carbohydrate metabolism, cognitive function, fertility and reproduction, macronutrient metabolism, metabolism of fatty acids, metabolism of vitamin A, protein synthesis, the maintenance of bones, the maintenance of hair, nails and skin, the maintenance of testosterone levels in the blood, the maintenance of vision, the function of the immune system, the protection of cells from oxidative stress and it has a role in the process of cell division
Amino Acid L-Tyrosine
This amino acid is precursor of several important neurotransmitters, including dopamine, that are important contributors to mood, cognitive performance as in combating stress.
L-tyrosine is also a precursor to the thyroid hormone, thyroxine (also known as T4) and supplementation may have a positive effect on thyroid hormone levels which help to contribute to an increased metabolic rate.
N-Acetyl L-Carnitine: (ALCAR, ALC or LAC) is a synthesized version of L-Carnitine, which is a derivative of the amino acids lysine and methionine.
Carnitine (generic name) is naturally present in animal products such as meat, fish, poultry, and milk and dairy products; small amounts are present in some plant foods. Almost all cells of the body contain carnitine, which transports fatty acids into the mitochondria, the power plants of our cells.
ALCAR helps:
Brain energy metabolism: LCAR helps the transport of fatty acids into mitochondria where they are used for energy metabolism. Mitochondria are the power plants of the body as their primary function is to generate the energy necessary to power our cells. Fuelling your cells power plants can boost physical and mental energy.
Neurotransmitters: ALCAR is a necessary ingredient for acetylcholine formation. Which boosts memory, mental alertness and fluid thought.
Brain optimisation: The antioxidant properties of Acetyl-L-Carnitine provides neuroprotective qualities, boosts Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF), and promotes cerebral blood circulation
Nootropic Functional Brain Foods & Nutrients
+
Ashwagandha
Gingko
Korean Panax Ginseng
Guarana
Green Tea
L-Theanine
Caffeine
Bacopa Monnieri
Rosemary Leaf
Curcumin
Cinnamon
Safety & Contraindications
Results may vary from person to person.
Store in a cool dry place, out of the reach of children.
Best before date: see base of container.
Caution: Do not exceed the recommended daily intake.
A food supplement should not be used as a substitute for a varied, balanced diet and healthy lifestyle.
Always consult your GP before taking food supplements if you are taking medication or have an existing medical condition.
If you feel unwell, stop taking this product immediately and seek medical advice.
References
References
Dietplan7.com. 2022. Home. [online] Available at: http://dietplan7.com/ [Accessed 28 March 2022].
Nawaz, A., Khattak, N., Khan, M., et al., (2020). Deficiency of Vitamin B12 and its relation with neurological disorders: a critical review. The Journal of Basic and Applied Zoology. 81 (1).
nhs.uk. (2022). Vitamin B12 or folate deficiency anaemia – Symptoms. [online] Available at: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/vitamin-b12-or-folate-deficiency-anaemia/symptoms/ [Accessed 28 March 2022].
O’Leary, F. and Samman, S., (2010). Vitamin B12 in Health and Disease. Nutrients, 2(3), pp.299-316.
Gandy, J., Madden, A. and Holdsworth, M., (2012). Oxford handbook of nutrition and dietetics. 2nd ed. United States: Oxford University Press Inc., New York, pp.116-117.
ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminB12-Consumer/
Vitamin B12 – Consumer (nih.gov)
Vitamin B12 related health claims | EFSA (europa.eu)
www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/pub/1756
Zinc related health claims | EFSA (europa.eu)
www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/pub/1819
Choline related health claims | EFSA (europa.eu)
Niacin related health claims | EFSA (europa.eu)
www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/pub/1224
Pantothenic acid related health claims | EFSA (europa.eu)
Pantothenic Acid – Consumer (nih.gov)
efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.2903/j.efsa.2009.1218
Folate related health claims | EFSA (europa.eu)
www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/pub/1760
Iodine related health claims | EFSA (europa.eu)
www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/pub/1214