



Liver Supplement
METABOLIC SUPPORT
£25.99
Metabolic Liver supplement with Choline, Biotin & synergistic nutrients Artichoke, NAC, ALA, Garlic, Liquorice & more to contribute to normal:
Liver Function
Lipid Metabolism
Homocysteine Metabolism
Macronutrient Metabolism
Energy-Yielding Metabolism



LIVER LOVER
Love Your Liver with Plant-Powered Goodness!

Liver Health
Nutrients to contribute to normal Liver Function

Metabolism Support
Supports Metabolic Health in Multiple Ways

Time to Detox
An Overburdened Liver Impacts Hormone Balance & Fat Loss

Detox Herbals
Traditional Liver-Loving Herbals Artichoke, Garlic, Liquorice Root & more
Liver Meta-Tox Benefits
Benefits
+
Liver Meta-Tox is a healthy liver supplement combining vitamins with traditional liver-loving herbal extracts formulated to support the liver and other detoxification organs and systems.
Lifestyle can have a significant impact on liver functioning, for example; alcohol consumption, high fat diet and pro-oxidative substances and synthetic drugs.
The liver is also the gland most vulnerable to the toxic effects of xenobiotics (such as pesticides, cosmetics, fragrances, food additives, industrial chemicals, environmental pollutants etc) as the liver is responsible for their metabolism.
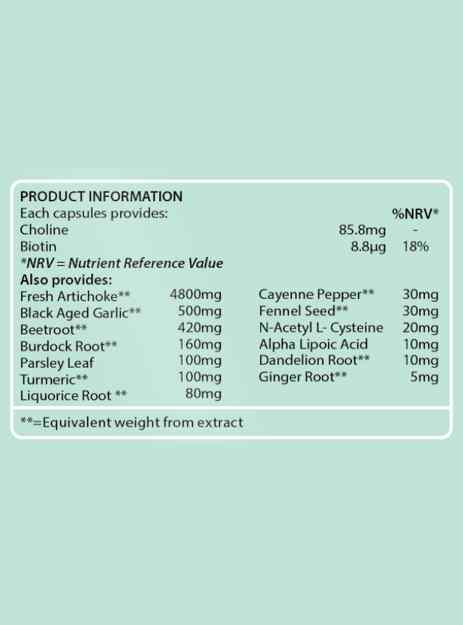
These liver support capsules contain:
choline
biotin
N-Acetyl L- Cysteine
Alpha Lipoic Acid (ALA)
artichoke
black aged garlic
beetroot
dandelion root
burdock root
parsley leaf
turmeric
liquorice root
cayenne
fennel seed
ginger root
Designed to support the liver and other detoxification organs and systems of the body and can be particularly useful during periods of over-indulgence in food, alcohol or smoking.
This comprehensive food supplement helps cleanse a congested liver and gallbladder and support cell repair and protection.
How many servings
+
Contains 60 Vegetarian Easy Take Capsules.
How to use
+
Take 1 capsule, 1 to 3 times per day or as required.
Warning: Contains NAC, which should not be used if peptic ulcers are present.
What’s Inside?
Artichoke
Artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) is a well known herbal medicine used in European medicine since the 18th century.
This ancient herbal treatment has been used to promote a healthy liver, efficient digestive system and healthy cholesterol levels.
Artichoke compounds have a protective effect on liver cells.
Extensively studied, artichoke extract contains the active ingredient, luteolin, and antioxidants caffeic acid, cynarin and cholorgenic acid.
These active ingredients protect liver cells from damage whilst stimulating the production of bile acid into the digestive tract. This in turn helps breaks down fats and has an effect on lowering high cholesterol levels and triglycerides.
Cynarin is the close botanical cousin of the herb milk thistle (which is also well-known for its positive effects on the liver).
Studies have shown that cynarin can:
reduce elevated triglycerides
lower total serum levels
increase beneficial HDL levels
Artichoke, therefore offers ideal support for the prevention of heart disease, while simultaneously cleansing liver cells.
Choline
Choline is a water-soluble vitamin, an essential nutrient found in many foods. The liver is a central organ responsible for choline metabolism.
Your brain and nervous system need it to regulate memory, mood, muscle control, and other functions. You also need choline to form the membranes that surround your body’s cells.
You can make a small amount of choline in your liver, but most of the choline in your body comes from your diet.
Studies show dietary consumption is important, as humans diets lacking choline develop fatty liver, liver damage and muscle damage. Hepatosteatosis and liver cell death occur when humans are deprived of choline
Choline contributes to normal lipid metabolism (the breakdown and storage of fats for energy).
Getting enough choline is necessary for proper liver function and to prevent Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Some studies have found a link between higher intakes of choline (and higher blood levels of choline) and better cognitive function (such as verbal and visual memory).
Choline contributes to normal:
homocysteine metabolism
lipid metabolism
maintenance of normal liver function
In the last few years, there have been significant advances in our understanding of the mechanisms that influence choline requirements in humans and in our understanding of choline’s effects on liver function.
Humans eating diets low in choline can develop fatty liver and liver damage. Fatty liver occurs in choline deficiency
The liver is the major organ within which methylation reactions occur. Choline influences liver function, and the dietary requirement for this nutrient varies depending on an individual’s genotype and estrogen status.
Alcohol also increases choline requirements of the liver.
Beetroot
Beetroot is a highly nourishing and cleansing vegetable.
Used for centuries as an effective natural cleanser of the liver, biliary system and gallbladder. It helps the liver to break down stored fats against cellulite and offers support for high energy levels and vitality.
A rich source of potent antioxidants and other nutrients, including dietary nitrate, selenium, magnesium, iron, sodium, potassium, vitamin C and betaine (which is important for cardiovascular health).
It also functions by acting with other nutrients to reduce the concentration of homocysteine, which can be harmful.
Biotin
Biotin is a water-soluble B-vitamin, also called vitamin B7 and formerly known as vitamin H or coenzyme R.
Biotin plays important roles in a variety of critical metabolic reactions in the cell. It is essential for human health, cell growth, the production of fatty acids and the metabolism of fats and amino acids.
Biotin contributes to normal:
energy-yielding metabolism
nervous system function
macronutrient metabolism
psychological function
hair and skin
maintenance of normal mucous membranes
Black Aged Garlic
Garlic has many beneficial properties and Black Aged Garlic is one of the oldest known natural remedies.
Black garlic contains more antioxidants than regular garlic.
It is an anti-bacterial, anti-parasitic, anti-spasmodic and anti-dyspeptic, and can have cholesterol lowering, triglyceride
lowering and blood pressure lowering actions.
Historically, it has been used to treat everything from dysentery, typhoid and cholera, to bacterial food poisoning, worms, colds and flu.
It helps to heal the bowel with its anti-bacterial actions and
is also used as a cholagogue, to stimulate bile.
Dandelion Root
Dandelion, a garden weed now grown globally, has long been consumed as a therapeutic herb.
Used for centuries, its folkloric uses include to treat liver, gallbladder, kidney and joint problems.
It is considered to be a blood purifier and is widely used to treat poor digestion, water retention and diseases of the liver, such as hepatitis.
It is a general stimulant to the system, and primarily used in connection with kidney and liver disorders. It’s believed to increases bile production in the gallbladder and bile flow from the liver.
This makes dandelion a great tonic for people with sluggish liver function due to alcohol or poor diet. The increase in bile flow can help improve fat (including cholesterol) metabolism in the body and it also cleanses the blood.
Dandelion is a source of potassium, sodium, calcium, phosphorus and iron.
The root contains bitter glycosides, tannins, triterpenes, sterols, volatile oil, choline, asparagin and inulin.
Dandelion is also rich in lecithin, also believed to protect the liver against cirrhosis.
Burdock Root
Burdock, (Arctium lappa), has been used therapeutically in Europe, North America and Asia for hundreds of years.
Burdock is promoted as a healthy and nutritive food in Chinese societies and is popular in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM).
Used traditionally as a hepatic (assists the liver in its functions and promotes the flow of bile), hepatoprotective, cholesterol reducer and
general detoxifier. Also a diuretic and can help with skin issues such as eczema, psoriasis and dermatitis
In the root, the active ingredients have been found to “detoxify” blood in terms of TCM and promote blood circulation to the skin surface, improving the skin quality and texture.
Antioxidants and antidiabetic compounds have also been found in the root. Its antibiotic-like actions will also assist in dealing with toxins circulating in the system.
As a potent lymph and skin cleanser, burdock forces the body to eliminate waste products, thereby clearing the skin, bloodstream and other organs and tissues of toxins.
This powerful blood purifier and potent detoxification herb, is partnered with dandelion for best effect.
Toxins that have been displaced by the burdock will need to be quickly eliminated by dandelion and the other herbs in this formula, which have been carefully chosen to partner burdock in its clearing actions.
Burdock root is also rich in Chlorogenic acid, a phenolic compound, which can regulate lipid (fat) metabolism.
Parsley Leaf
Parsley (Petroselinum crispum) is a popular medicinal plant widely used in different traditional medicines all over the world.
An important medicinal plant with wide range of proven medicinal activity. Parsley is a natural anti-spasmodic, a carminative, gastro tonic, a good expectorant and traditionally used as a diuretic, liver and stomach tonic, used for coughs and asthma, indigestion and may also help relieve gas.
Parsley helps to cleanse the liver, kidneys (breaks down gallstones and kidney stones) and bloodstream. It’s green leaves contain chlorophyll – a powerful phyto-chemical, detoxifier and cleanser.
Research has identified a wide range of pharmacological activity including:
antioxidant
hepatoprotective
brain protective
anti-diabetic
analgesic
spasmolytic
immunosuppressant
anti-platelet
gastroprotective
cytoprotective
laxative
estrogenic
diuretic
hypotensive
antibacterial
antifungal
Turmeric
Turmeric (Curcuma longa L.) has been used in herbal medicine in traditional medical schools, including Islamic traditional medicine, Chinese traditional medicine, and Ayurveda for thousands of years.
Curcumin has been used in ayurvedic medicine as a blood purifier, for digestive problems, stomachic, carminative, bile stimulant and in particular to strengthen liver function and treat hepatitis C and gallbladder disease.
The yellow pigment in turmeric, called curcumin is:
anti-inflammatory
antioxidant
anti-diabetic
controls obesity and metabolic problems
improves memory and mood disorders
used as herbal medicine for treating liver diseases
The liver is the main organ for metabolic and detoxification reactions in the body. Therefore, its diseases can be associated with both metabolic disorders, such as insulin resistance, obesity, diabetes, or dyslipidemia, and exogenous insults such as drugs, xenobiotics, or alcohol. Turmeric /curcumin is believed to possess therapeutic features in ameliorating various metabolic disorders.
Curcumin is proposed to have a positive impact on patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
Several studies reported that curcumin supplementation could improve non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
It’s beneficial effects include:
improving liver function
decreasing serum TG levels
ameliorating insulin resistance
reducing obesity
Therapeutically, curcumin exhibits promising potential in preclinical and clinical studies and is currently in human trials for a variety of conditions, including metabolic syndrome, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, rheumatoid arthritis, migraine, premenstrual syndrome, ulcerative colitis, knee osteoarthritis, polycystic ovarian syndrome, atherosclerosis, liver cirrhosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, depression, psoriasis, and Alzheimer’s disease.
Liquorice Root
Liquorice root is a medicinal plant with a long history of use, going back to ancient Assyrian, Egyptian, Chinese and Indian cultures.
Liquorice is one of the most commonly used herbal drugs in Traditional Chinese Medicine for the treatment of liver diseases and drug-induced liver injury (DILI).
Liquorice’s liver-loving bioactive components include:
glycyrrhizin
glycycoumarin
Glycyrrhizin has anti-inflammatory, anti-viral and anti-allergic properties. Studies show that Glycyrrhizin can inhibit liver cell injury caused by many chemicals and is used in the treatment of chronic hepatitis, hepatitis B and cirrhosis in Japan.
Glycycoumarin (GCM) is a coumarin compound in liquorice. Recent studies demonstrate that GCM is highly effective against liver conditions including alcoholic liver disease and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Liquorice’s other potential benefits may include:
Adrenal Exhaustion: It’s main active ingredient Glycyrrhizin, inhibits cortisol breakdown, thereby helping to restore normal levels of this ‘stress’ hormone.
Soothing Properties: Liquorice root may help soothe sore throats and coughs due to its natural demulcent properties.
Digestive Aid: Used traditionally to aid digestion and alleviate symptoms of indigestion by helping reduce inflammation in the stomach lining.
Hormone Regulation: Liquorice root may help regulate hormone levels and is sometimes used to manage menopause symptoms and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
Caution: not to be used in cases of untreated high blood pressure, due to its effect on aldosterone.
Cayenne
Cayenne is regarded by herbalists as the purest and safest stimulant, cayenne opens up tissues throughout the body to an increased flow of blood and stimulates the oxygenation of cells and organs.
It invigorates the circulatory system and the heart to work more efficiently and thereby assists the effective movement of toxins out of the body.
It also serves as a carrier for the other herbs in this formula – so that they arrive quickly and effectively to their particular areas of work.
Capsaicin (CAP) is the main component responsible for the pungency (burning pain) of the chili plant (capsicum spp.), whose metabolic functions include thermogenic to increase:
fat oxidation
energy balance
fatty acid oxidation
Fennel Seed
Fennel seed act as a gentle warming agent for delicate stomachs.
Fennel is also a carminative, aromatic, anti-spasmodic, antibacterial, antifungal, digestive and gut soother, which has mild stimulant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Fennel is packed full of fibre and important nutrients such as vitamin C, calcium, magnesium, potassium and manganese.
Appetite Control
Fennel is also used to help curb appetite.
A study of healthy women found that those who drank 250 ml of tea made with 2 grams of fennel seeds before eating were significantly less hungry and consumed fewer calories during the meal than those who drank a placebo tea.
Hormone Balance
Fennel also has strong estrogenic properties, meaning that it acts similar to the hormone estrogen.
A review of 10 studies found that fennel may improve sexual function and satisfaction in menopausal women, as well as relieve hot flushes, sleep disturbances along with other menopause symptoms.
N-Acetyl L- Cysteine (NAC)
N-Acetyl L-Carnitine: (ALCAR, ALC or LAC) is a synthesized version of L-Carnitine, which is a derivative of the amino acids lysine and methionine.
NAC is a powerful antioxidant and is also a precursor to glutathione, the body’s most abundant antioxidant, found in virtually every cell.
Carnitine (generic name) is naturally present in animal products such as meat, fish, poultry, and milk and dairy products and in small amounts in some plant foods.
Almost all cells of the body contain carnitine, which transports fatty acids into the mitochondria, the power plants of our cells.
NAC works by helping to eliminate free radicals and heavy metals from the body and in turn improves cellular health.
NAC helps the body to neutralise toxins and is a chelator of heavy metals (such as mercury from dental amalgam fillings, cadmium and lead from paint and cigarette smoke).
Toxic metals can accumulate in the body over time and continue to cause free radical damage as long as they remain.
It’s sulphur content has also been linked to enhanced resistance to viral infections. Studies show that it may protect the body against ailments such as bronchitis, asthma, emphysema and sinusitis.
Animal studies have also shown that NAC can prevent damaging changes to DNA caused by the dangerous chemicals in cigarette smoke. For those who smoke or have smoked, this is a must-take supplement.
Animal studies have also found that N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) could effectively reduce binge drinking-induced fatty liver.
NOTE: do not use NAC if peptic ulcers are present
Alpha Lipoic Acid (ALA)
Alpha Lipoic Acid (ALA) or Lipoic acid, is known as the “universal antioxidant”.
It is a vitamin-like substance naturally produced in the body and plays a unique role in defending against free radical damage.
It’s great antioxidant potential make it useful for scavenging free radicals, chelates metals, and restoring intracellular glutathione (another important antioxidant) levels which otherwise decline with age.
Like NAC (above), ALA can also be found in our mitochondria – the body’s power plants.
More than 20 years ago it was discovered that lipoic acid could cure a fatal liver disease caused by the ingestion of the highly poisonous Amanita mushrooms.
The liver damage caused by the free radicals present in these mushrooms destroys liver cells, and 90% of people who eat them will die. However, intake of lipoic acid cured these patients, confirming its powerful liver cleaning and protective properties.
ALA also helps to stabalise blood sugar levels and insulin resistance – a common complaint in middle-aged men and women – which can lead to a range of serious health problems.
Athletes report that they experience far less muscle soreness following exercise, when taking ALA.
Ginger Root
Ginger has been used for thousands of years for the treatment of numerous ailments, such as colds, nausea, arthritis, migraines, and hypertension.
A warming herb, it helps to ensure that toxins are kept circulating until properly eliminated.
It is also calming to the stomach and can help combat feelings of nausea, which may be produced during the detox process.
Its actions include anti-inflammatory, carminative, anti-spasmodic, expectorant, vasodilator, circulatory system stimulant and anti-cholesterol.
Ginger helps to alleviate occasional gas and bloating and is known as a ‘hot bitter’ herb which promotes gastric acidity, gastric secretions and aids in digestion.
As such, it is used for a range of stomach conditions. For example, it is used for flatulence and in cases of achlorhydria (absence or reduction of hydrochloric acid in stomach juices).
Ginger is also being studied in respect to fatty acid liver disease (FLD). Fatty liver disease (FLD) is the most common chronic liver disease worldwide. The pathogenesis of this disease is closely related to obesity and insulin resistance.
Ginger has hypolipidemic and antioxidant effects and acts as an insulin sensitizer and studies show that Ginger may reduce many clinical aspects of FLD via:
insulin-sensitive effects
stimulating the expression of antioxidant enzymes
reducing the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS)
having anti-dyslipidemic activities
reducing hepatic fat content
Safety & Contraindications
Results may vary from person to person.
Store in a cool dry place, out of the reach of children.
Best before date: see base of container.
Caution: Do not exceed the recommended daily intake.
A food supplement should not be used as a substitute for a varied, balanced diet and healthy lifestyle.
Always consult your GP before taking food supplements if you are taking medication or have an existing medical condition.
If you feel unwell, stop taking this product immediately and seek medical advice.
References
Medicinal Plant-Derived Phytochemicals in Detoxification – PubMed (nih.gov)
A review of the pharmacological effects of Arctium lappa (burdock) – PubMed (nih.gov)
Biotin: biochemical, physiological and clinical aspects – PubMed (nih.gov)
Insights on the Use of α-Lipoic Acid for Therapeutic Purposes – PubMed (nih.gov)
Alpha-lipoic acid as a dietary supplement: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential – PubMed (nih.gov)
[Protective effects of N-acetyl-L-cysteine against binge drinking-induced fatty liver in mice] – PubMed (nih.gov)
Choline’s role in maintaining liver function: new evidence for epigenetic mechanisms – PubMed (nih.gov)
Choline metabolism provides novel insights into non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its progression – PubMed (nih.gov)
Choline related health claims | EFSA (europa.eu)
Choline – Consumer (nih.gov)
Influence of alcohol and choline deficiency upon rat liver uptake of choline – PubMed (nih.gov)
[Artichoke–herbal drug] – PubMed (nih.gov)
[Artichoke–untapped potential of herbal medicine in the treatment of atherosclerosis and liver diseases] – PubMed (nih.gov)
Pharmacological Studies of Artichoke Leaf Extract and Their Health Benefits – PubMed (nih.gov)
Review – Glycyrrhiza glabra L. (Liquorice) – PubMed (nih.gov)
Glycyrrhiza Genus: Enlightening Phytochemical Components for Pharmacological and Health-Promoting Abilities – PubMed (nih.gov)
Preclinical Evidence for the Pharmacological Actions of Glycyrrhizic Acid: A Comprehensive Review – PubMed (nih.gov)
Protective effects of glycycoumarin on liver diseases – PubMed (nih.gov)
Natural products in licorice for the therapy of liver diseases: Progress and future opportunities – PubMed (nih.gov)
Curcumin: A Review of Its Effects on Human Health – PubMed (nih.gov)
Turmeric and Curcumin: From Traditional to Modern Medicine – PubMed (nih.gov)
Efficacy of curcumin/turmeric on liver enzymes in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials – PubMed (nih.gov)
Effects of curcumin/turmeric supplementation on the liver enzymes, lipid profiles, glycemic index, and anthropometric indices in non-alcoholic fatty liver patients: An umbrella meta-analysis – PubMed (nih.gov)
The effects of curcumin supplementation on liver function, metabolic profile and body composition in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials – PubMed (nih.gov)
Evidence-based herbal treatments in liver diseases – PubMed (nih.gov)
Effects of curcumin in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis – PubMed (nih.gov)
graecum) Tea Drinking Suppresses Subjective Short-term Appetite in Overweight Women. Clin Nutr Res. 2015 Jul;4(3):168-74. doi: 10.7762/cnr.2015.4.3.168. Epub 2015 Jul 31. PMID: 26251835; PMCID: PMC4525133.
Effect of Fennel on the Health Status of Menopausal Women: A Systematic and Meta-analysis – PubMed (nih.gov)
Fennel (Foeniculum vulgare) and Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) Tea Drinking Suppresses Subjective Short-term Appetite in Overweight Women – PubMed (nih.gov)
Petroselinum crispum (Mill.) Fuss (Parsley): An Updated Review of the Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacology – PubMed (nih.gov)
Parsley: a review of ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and biological activities – PubMed (nih.gov)
Medicinal Plant-Derived Phytochemicals in Detoxification – PubMed (nih.gov)
The potential of dandelion in the fight against gastrointestinal diseases: A review – PubMed (nih.gov)
Therapeutic Application of Betalains: A Review – PubMed (nih.gov)
A systematic review and meta-analysis of preclinical and clinical studies on the efficacy of ginger for the treatment of fatty liver disease – PubMed (nih.gov)
The Amazing and Mighty Ginger – Herbal Medicine – NCBI Bookshelf (nih.gov)
Molecules | Free Full-Text | Capsaicin: Current Understanding of Its Mechanisms and Therapy of Pain and Other Pre-Clinical and Clinical Uses (mdpi.com)
Nutrients | Free Full-Text | Spices for Prevention and Treatment of Cancers (mdpi.com)
Capsaicinoid nonivamide improves nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in rats fed a high-fat diet – PubMed (nih.gov)